- TECHNÉTIUM
- TECHNÉTIUMTECHNÉTIUMDu grec tekhnétos , artificiel.Symbole chimique: TcNuméro atomique: 43Masse atomique: 98,9 gPoint de fusion: 2 172 0CPoint d’ébullition: 4 877 0CDensité (à 20 0C): 11,5Métal du groupe du manganèse produit artificiellement pour la première fois en 1937 par C. Perrier et E. G. Segrè, sous la forme de son isotope 97 pratiquement stable (période de 2 600 000 ans), après irradiation aux deutons du molybdène. Son isotope 99 (période 212 000 ans) est obtenu comme produit de fission dans les réacteurs nucléaires et il est isolé par la technique des échangeurs d’ions; c’est une poudre grise, mais le métal cristallisé ressemble au platine et devient supraconducteur au-dessous de 11,2 k.P. W. Merrill a décelé la présence de technétium 99 dans les étoiles du type S par spectroscopie, ce qui présente un grand intérêt pour l’astrophysique et la nucléosynthèse.On a préparé des quantités importantes de technétium par décomposition thermique ou par électrolyse du pertechnétate d’ammonium; ses sels sont analogues à ceux du rhénium; ses alliages sont efficaces contre la corrosion.
technétium [ tɛknesjɔm ] n. m.• 1937; appelé masurium à sa découverte en 1925; du gr. sav. tekhnêtos « artificiel »♦ Chim. Élément atomique radioactif artificiel (Tc; no at. 43; m. at. 98,90).
● technétium nom masculin (grec tekhnêtos, artificiel) Métal de numéro atomique 43, dont un isotope radioactif, le technétium 99 m, est le traceur le plus utilisé en médecine nucléaire (plus de 80 % des scintigraphies).technétiumn. m. CHIM élément radioactif artificiel (symbole Tc) de numéro atomique Z = 43. (L'isotope de masse atomique 99 a une période de l'ordre de 10 6 années.)— Métal (Tc), utilisé notamment en scintigraphie.⇒TECHNÉTIUM, TECHNÉCIUM, subst. masc.CHIM. NUCL. ,,Élément radioactif (...) obtenu par les réactions utilisées en radioactivité artificielle`` (UV.-CHAPMAN 1956). Cet élément, qui fut ensuite trouvé dans certains produits de fission de l'uranium, fut nommé technécium par Segré et Perrier en 1947 (Hist. gén. sc., t. 3, vol. 2, 1964, p. 425). Le technétium est un corps simple de symbole Tc, de numéro atomique 43, de nombre de masse 99, de poids atomique 98,913 (Encyclop. Sc. Techn. t. 10 1973, p. 274).Prononc. et Orth.:[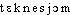 ]. Une forte majorité des suj. MARTINET-WALTER 1973 disent -tium [-
]. Une forte majorité des suj. MARTINET-WALTER 1973 disent -tium [-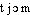 ]. Lar. Lang. fr.:[-netium]. Étymol. et Hist. 1953 (Lar. 20e Suppl.). Dér. sav. du gr.
]. Lar. Lang. fr.:[-netium]. Étymol. et Hist. 1953 (Lar. 20e Suppl.). Dér. sav. du gr. 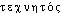 « artificiel »; suff. sc. -ium. Mot créé par les physiciens PERRIER et SEGRÉ in Nature, 4 janv. 1947, 24-1 ds NED Suppl.2: We would like to propose the name of ,,technetium`` from the Greek
« artificiel »; suff. sc. -ium. Mot créé par les physiciens PERRIER et SEGRÉ in Nature, 4 janv. 1947, 24-1 ds NED Suppl.2: We would like to propose the name of ,,technetium`` from the Greek 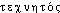 , artificial, in recognition of the fact that technetium is the first artificially made element.technétium [tɛknesjɔm] n. m.ÉTYM. 1937; appelé masurium à sa découverte (1925); dér. sav. du grec teckhnêtos « artificiel ».❖
, artificial, in recognition of the fact that technetium is the first artificially made element.technétium [tɛknesjɔm] n. m.ÉTYM. 1937; appelé masurium à sa découverte (1925); dér. sav. du grec teckhnêtos « artificiel ».❖
Encyclopédie Universelle. 2012.
